Search for answers or browse our knowledge base.
-
Behaviour Scoring
-
- 1. Anxious in unfamiliar situations
- 2. Fear Of Noises
- 3. Fear of Novel Objects
- 4. Fear of Underfootings
- 5. Fear of Dogs
- 6. Fear of Stairs
- 7. Fear of Traffic
- 8. Separation Anxiety
- 9. Hyper-Attachment
- 10. Fear Of Strangers
- 11. Body Handling Concern
- 12. Retreats When Reached For
- 13. Harness Handle On Back Sensitivity
- 14. Avoidance Of Blowing Fan
- 15. Body Sensitivity To Object Contact
- 16. Anxious About Riding In Vehicles
- 17. Inhibited or passively avoidant when exposed to potentially stressful situations
- 18. Activated when exposed to potentially stressful situations
- 19. Excitable
- 20. Slow To Return To Productive Emotional State
- 21. Fidgety When Handler Is Idle
- 22. Fear On Elevated Areas, Drop-Offs Etc.
- 23. Barks Persistently
- 24. High Energy Level
- 25. Lacks Focus
- 26. Movement Excites
- 27. Chasing Animals
- 28. Dog Distraction
- 29. Sniffing
- 30. Scavenges
- 31. Inappropriate Behavior Around The Home
- 32. Lacks Initiative
- 33. Not Willing
- 34. Resource Guarding Toward People
- 35. Aggression Toward Strangers
- 36. Aggression Toward Dogs
- 37. Resource Guarding Toward Dogs Or Other Pets
- 38. Inappropriate Elimination While Working En Route
- 39. Socially Inappropriate Behavior With People
- 40. Inconsistent
- 41. Handler/Dog Team
- 42. Relationship Skills
- 43. Comparison 9 To 1 Score
- 44. Socially Inappropriate Behavior With Dogs
- 45. Thunder Reaction Prior To, During Or Immediately After A Thunderstorm
- 46. Kennels Poorly
- 47. Working Speed
- 48. Gait When Moving Out
- 49. Housebreaking Problems
- 50. Innate Desire To Work
- 51. Avoidance Of Exhaust From Vehicles
- Show all articles ( 36 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
Practice Videos
-
Behavior Testing
-
Database User Manual
-
-
-
- Adding a New Dog (using Manage Your Dog’s Data, MyDogs)
- Alerts
- BCL, Behavior Checklist
- Elbow Quick, Add new
- Estrus & Whelps
- Eye Quick
- Genetic Test Panel
- Genetic Test Quick
- Health Diagnoses Add/Edit
- Health History Report
- Health Normals, Add new
- Heart Quick
- Hip BVA, Add new
- Hip FCI, Add new
- Hip OFA, Add new
- Hip Penn Hip, Add new
- Photos PDFs etc.
- Private Notes
- Procedures, Add new
- Reminders
- Share my dog data to another organization
- Skin Quick
- Status History
- Weight - Entering a dog's weight
- ADI Public Access Test
- Hip Vezzoni, Add new
- Status Detail
- Edit or Change Call Name / Pedigree Name / Owner ID
- Add New Microchip / Delete Incorrect Microchip
- End Reasons
- Juvenile Estrus
- Communications Activities
- Incidents
- Show all articles ( 18 ) Collapse Articles
-
- Articles coming soon
-
-
-
-
- Alternate Therapy/Rehab
- Diagnostic Imaging, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Diet
- Elbow Quick, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Estrus & Whelps, Add new
- Eye Quick, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Genetic Test Quick, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Health Diagnoses, Add new / Edit (Update) or Delete
- Health History Report, Generate a PDF
- Health Normals
- Health Screening List
- Hip OFA Add new / Edit or Delete
- Hip Penn Hip Add new / Edit or Delete
- Hospitalization, Add new
- Kennel Tasks, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Lab, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Photos, PDFs, etc., Add new
- Reminders Add new / Edit or Delete
- Rx, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Semen Cryo, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Skin Quick Add new / Edit or Delete
- SOAP, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Status History
- Supplies Used, Add new / Edit or Delete
- Surgery, Add new
- Treatments Add new / Edit or Delete
- Vaccines Add new / Edit or Delete
- Weight and BCS Body Condition Score - Add new / Edit or Delete
- Hip Vezzoni, Add new
- Show all articles ( 14 ) Collapse Articles
-
-
-
-
Early Socialization
-
- Video - Coat Desensitization
- Video - Novel Objects
- Video - Trolley Ride with Mom
- Early Puppy Socialization - Novel Objects video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Novel Sounds video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Introducing New Environments video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Motor Development, Balance, Coordination, Proprioception video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Passive Environmental Enrichment in the Den video
- Early Puppy Socialization – Stairs
-
-
Genetic Selection & Inbreeding
-
- What are EBVs and how do they help?
- How EBVs are calculated
- What is needed to calculate EBVs and EBV accuracy?
- Using EBVs effectively
- Selection index
- Why are EBVs different for littermates?
- Presentation Recording: Improving behavior using EBVs
- Presentation Recording: Using EBVs successfully
- Presentation Recording - Improving health using EBVs
-
Webinars
-
Reproduction
-
Organization Management
Organizational Traction – Setting the vision
0 out of 5 stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |
Organizational Traction: Setting the Vision and the Steps/Tools to Achieve It
Setting the Vision
The vision statement is a narrower, future-oriented declaration of the organization’s purpose and aspirations compared to an organization’s mission statement. Vision statements answer the question “Where is this organization going?” Vision statements also provide a bridge between the mission and the priorities. The best vision statements create a tension and restlessness with regard to the status quo—that is, they should foster a spirit of continuous innovation and improvement within an organization. Turn the vision statement into actionable items by setting goals and objectives.
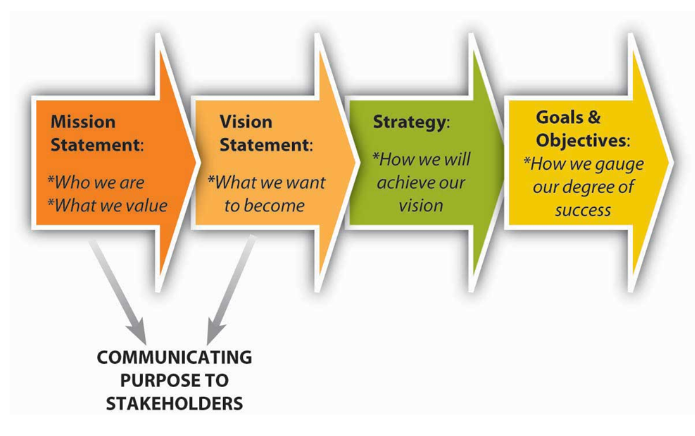
(University of Minnesota (n.d.). Principles of Management. Https://Open.lib.umn.edu/Principlesmanagement/. Retrieved March 10, 2023, from https://open.lib.umn.edu/principlesmanagement/chapter/4-3-the-roles-of-mission-vision-and-values/)
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are individuals or groups who have an interest in an organization’s ability to deliver intended results and maintain the viability of its products and/or services. They can be anyone from anywhere: leadership team, staff, volunteers, donors, vendors, clients, or outside influencers. Industry examples include clients who expect a quality product and know that their dog was produced/raised/trained in an ethical way, breeder hosts who want to know the breeding program is using best practices, or puppy raisers who want to know they will be supported throughout the puppy’s stay in their houses to name a few.
To successfully get key stakeholders to buy into the vision, include them in the vision setting process from the start. Make it easy for everyone to participate in creating, redrafting, and giving feedback in the vision setting process. Maintain constant communication throughout the process and request multiple ideas prior to meetings. Hold stakeholders accountable by asking them to come to the table with new concepts. Always take a forward-thinking approach and accept out-of-the-box ideas. Having the key stakeholders help draft the vision will make them more committed to its fulfillment.
Prioritization Matrix
When looking at what needs to happen to make a vision a reality, it’s important to prioritize what is needed for success. A basic tool to help is utilizing a prioritization matrix. In principle, the benefits of a prioritization matrix are quite straightforward. In support of structured decision-making, they make it easy to break down and prioritize complex issues when there are multiple factors influencing the decision and can help objectively and unambiguously rank your priorities. It can be applied to anything, from simple tasks to complex projects, and used by anyone, from single individuals to large organizations. A prioritization matrix provides stakeholders with a reliable process for resolving disagreements and deciding on which proposals to focus on. They also help to weed out disingenuous incentives and hidden agendas, in the case of project prioritization, by promoting consensus. They help make quarterly and annual plans that result in the highest impact, given the resources available.
Creating a prioritization matrix starts with making a list of all unsorted priorities and ends with that same list ordered by some quantifiable metric. In example below, priorities are sorted into 4 categories ranked 1 to 4:
- high benefit/value, low cost/effort
- high benefit/value, high cost/effort
- low benefit/value, low cost/effort
- low benefit/value, high cost/effort
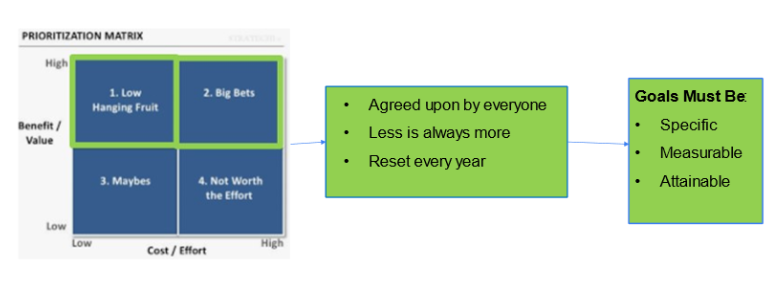
After creating a prioritization matrix, it’s important that the goals created are agreed upon by all stakeholders. Goals should be specific, measurable, and attainable. Less is more when it comes to setting goals. Teams can easily become overwhelmed if too many priorities/goals are given to them at once.
Obstacles, Concerns and Opportunities
Consider all aspects when setting goals. Obstacles, concerns, and opportunities are three key influences when it comes to achieving goals and the overall vision. All three influences can be found in the quality of people within/around the organization, funding, and operational efficiency.
Obstacles can be anything from staffing limitations (number of, quality of, distribution of), capacity issues (buildings, number of kennels, size of puppy raiser population), budgeting, and many more. It’s important to consider known and theoretical or potential obstacles when setting goals. Below are some tools to help understand known or potential obstacles:
- Tools to Manage a Breeding Colony: https://www.iwdr.org/master-knowledge-base/tools/
- Production Planning: https://www.iwdr.org/master-knowledge-base/production/
- IGDF Resources: https://www.igdf.org.uk
- IGDF Knowledgebase: https://igdf-education.org/moodle/
- ADI Resources: https://assistancedogsinternational.org/resources/resources/
Another obstacle is operational efficiency. Operating efficiently means using resources like time, people, equipment, inventory and money in an optimized way to serve the business. Efficient companies are leaner, agile and more profitable. One way to become more effective is to use data to prioritize what needs attention or improvements. IWDR is an online resource that collects data for health and temperament and can be used to improve an organization’s breeding colony, grow dog placements and success, and even expand its knowledge in multiple areas including reproduction, puppy socialization and development, and behavior and temperament. The links below will help introduce you to all that IWDR has to offer:
- IWDR Knowledge Base: https://www.iwdr.org/master-knowledge-base/
Concerns from key stakeholders should also be considered in goal setting. Making sure all parties are communicating and on the same step is important to reach the best possible outcome.
Opportunities come in all shapes and sizes. They can show up as a chance to gain knowledge and grow, or pivot away from a policy or long held tradition if it means embracing a new goal, or even focusing on a small detail that will end up leaving a larger impact.
Right People in the Right Seats
The success of an organization is dependent on having the right people in the right seats. This relates to not only staff, but also volunteers, donors, clients, vendors and other people that interact with or help support the organization. Looking for people with leadership skills, who can hold themselves and others accountable, and who want to build and grow within the organization’s vision creates a culture that is supportive while effective.
Create, Problem Solve, and Change
Creating standard operating procedures can keep a program’s day-to-day management on track, help resolve issues, overcome obstacles, and help an organization reach their goals. A standard operating procedure (SOP) is a step by step, repeatable process for any given routine task. Implementing SOPs help prevent user stress, mistakes, and miscommunication while ensuring reliability and consistency. When creating SOPs, always keep in mind the scope of the task and the end user. The scope of the task should be clearly stated at the beginning of the process with who it impacts, who are the users, and what is the end goal. To do this, use concise and clear language, keeping tasks simple but thorough. Utilize intuitive formatting: does the process lend itself to a checklist? Flow chart? Step by step list? A functional SOP should tell users where they need to be, what they need to do and give the users confidence in the task given.
Communication is key when executing a vision. It is essential to create a workplace where people are comfortable calling out the issues and working together to problem solve. To keep from getting overwhelmed or swamped by the details when it comes to problem solving issues, identify the top three issues to work on. From that list create the end solutions that would mean the problem has been resolved. Take those solutions and work backwards to get actionable items and realistic timeframes. A person’s, departments, or even organization’s ability to succeed is directly proportional to its ability to effectively problem solve.
Change management is the process that organizations use to implement changes through building and delivering effective change strategies. It includes reviewing reasons for change, implementing changes, and helping people adapt to these changes. Changes could be staff structure, introducing new technology, reducing costs, increasing profits, or a combination of items to reach a desired goal.
Prepare key stakeholders via education and communication. Explain why changes are happening clearly to reduce uncertainty. Create dissatisfaction with the status quo so stakeholders are willing to open up to the idea of change. For example, industry best practices for artificial insemination used to be a French catheter. However, with advances in technology transcervical insemination is now considered the industry standard.
Throughout the process celebrate milestones, energize and communicate with stakeholders and opportunities to succeed. Reward adaptors and provide support for the people struggling as trust and relationship building are an important part of creating a successful change process.
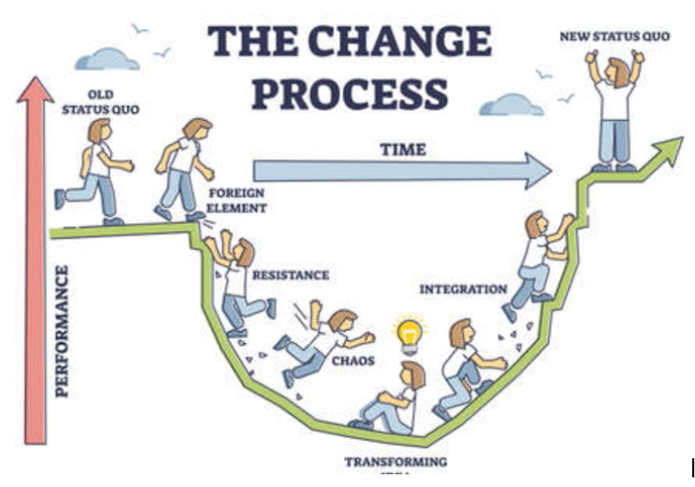
Conclusion
Creating a culture that rewards innovation, embraces change, clear communication, works with quality people, prioritizes problem solving, and sets achievable goals will help any organization succeed in executing their vision. Organizational traction begins when you seek change. Below are additional reading and resources that might be helpful to get started:
- Traction: Get A Grip on Your Business by Gino Wickman
- Principles of Management by University of Minnesota
- What data should I collect?
- Production Planning
- Introduction to Genetic Selection
0 out of 5 stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |
